Abstract What is the unit of analysis in economics? The prevailing orthodoxy in mainstream economic theory is that the individual is the ‘ultimate’ unit of analysis. The implicit goal of mainstream economics is to root macro-level social structure in the micro-level actions of individuals. But there is a simple problem with this approach: our knowledge […]
Continue Reading2018/02: Fix, ‘A Hierarchy Model of Income Distribution’
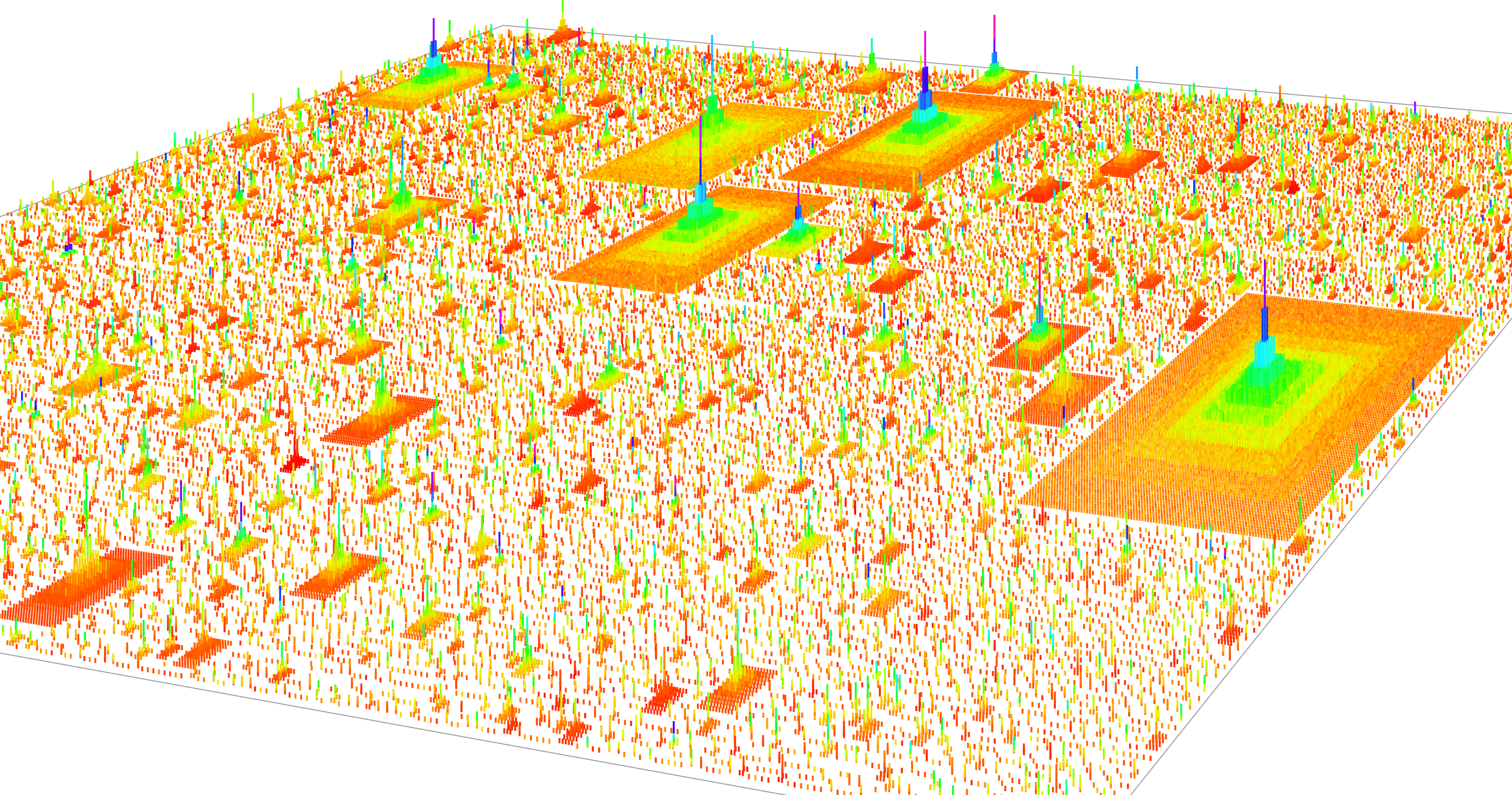
Abstract Based on worldly experience, most people would agree that firms are hierarchically organized, and that pay tends to increase as one moves up the hierarchy. But how this hierarchical structure affects income distribution has not been widely studied. To remedy this situation, this paper presents a new model of income distribution that explores the […]
Continue ReadingNo. 2017/03: Fix, ‘Evidence for a Power Theory of Personal Income Distribution’
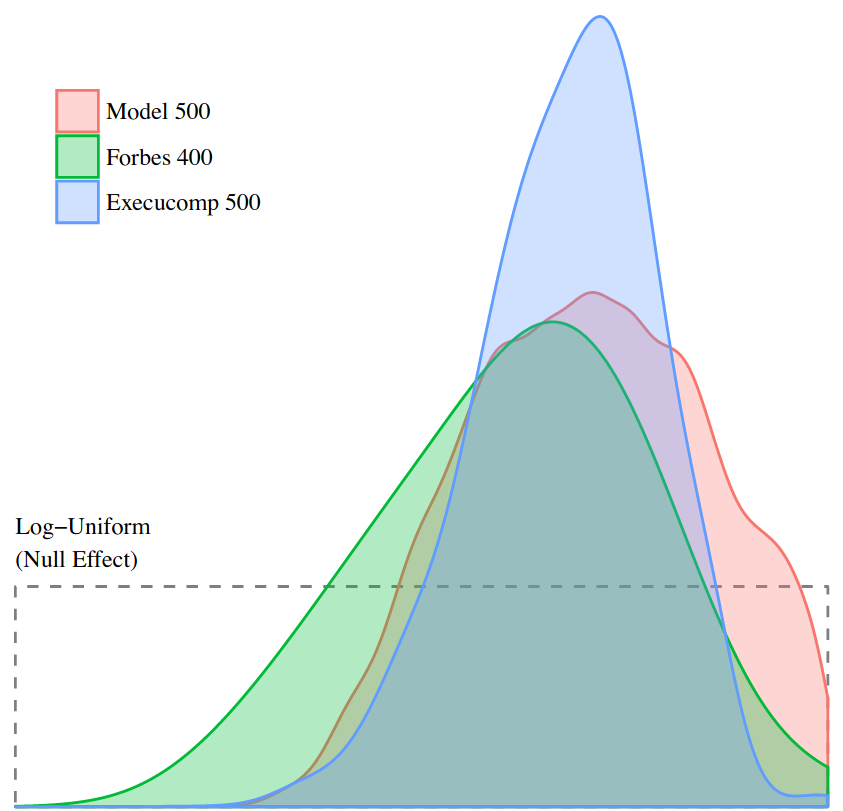
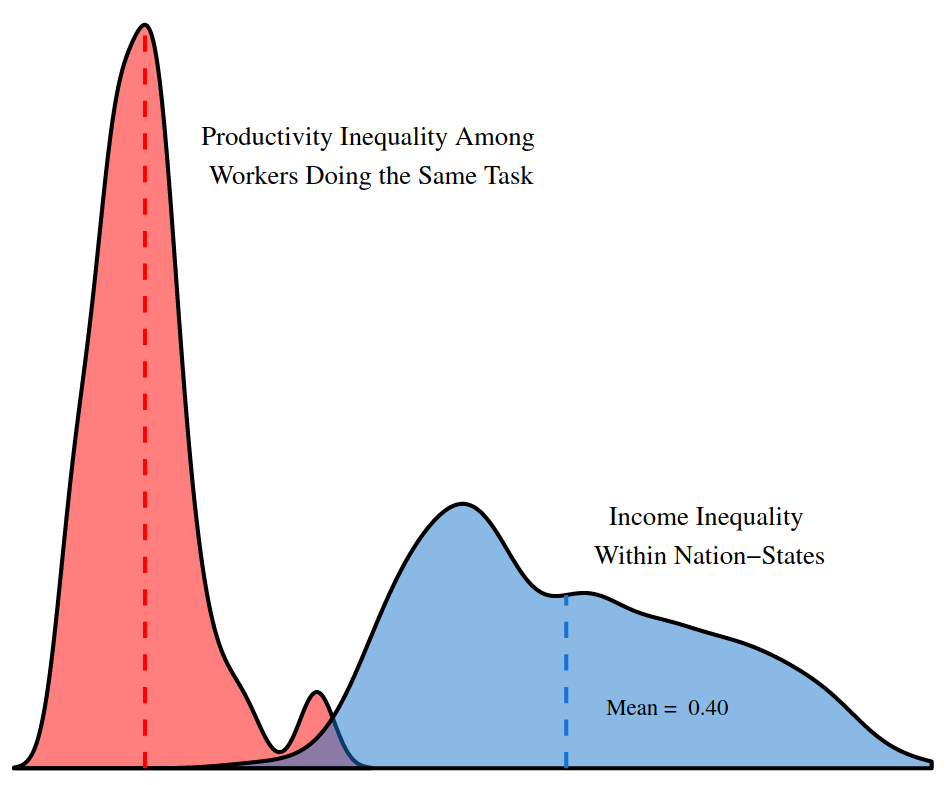
Abstract This paper proposes a new ‘power theory’ of personal income distribution. Contrary to the standard assumption that income is proportional to productivity, I hypothesize that income is most strongly determined by social power, as indicated by one’s position within an institutional hierarchy. While many theorists have proposed a connection between personal income and power, […]
Continue ReadingHager, ‘Public Debt, Inequality, and Power: The Making of a Modern Debt State’
Abstract Who are the dominant owners of US public debt? Is it widely held, or concentrated in the hands of a few? Does ownership of public debt give these bondholders power over our government? What do we make of the fact that foreign-owned debt has ballooned to nearly 50 percent today? Until now, we have […]
Continue ReadingPutting Power Back into Growth Theory
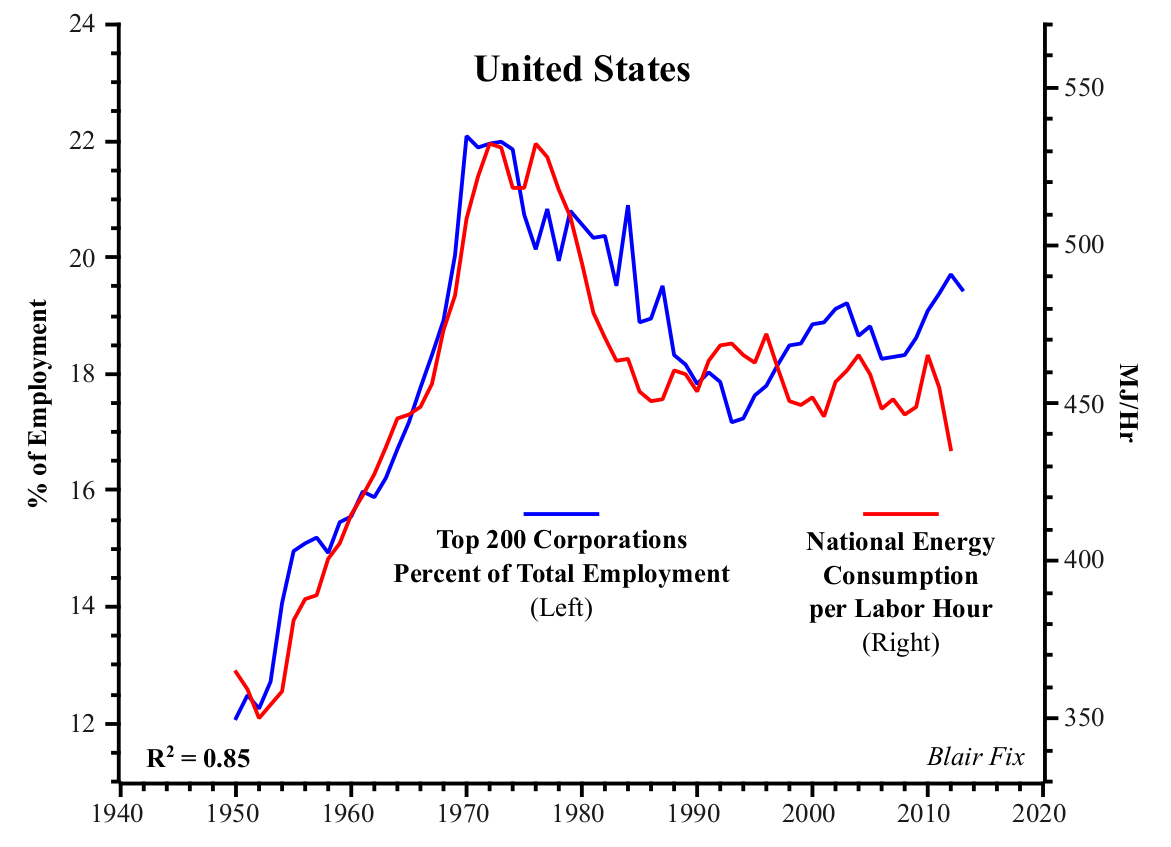
Putting Power Back Into Growth Theory BLAIR FIX June 2015 Abstract Neoclassical growth theory assumes that economic growth is an atomistic process in which changes in distribution play no role. Unfortunately, when this assumption is tested against real-world evidence, it is systematically violated. This paper argues that a reality-based growth theory must reject neoclassical principles […]
Continue Reading