Originally published at joefrancis.info Joe Francis When a prominent economic historian provides a new estimate of something, it is likely that the estimate will be taken at face value. Other economic historians will cite it, so it becomes reified, until it is treated as fact, even when it is little more than fancy. John Coatsworth’s […]
Continue ReadingThe ‘Reversal of Fortune’: Institutions or Globalisation?
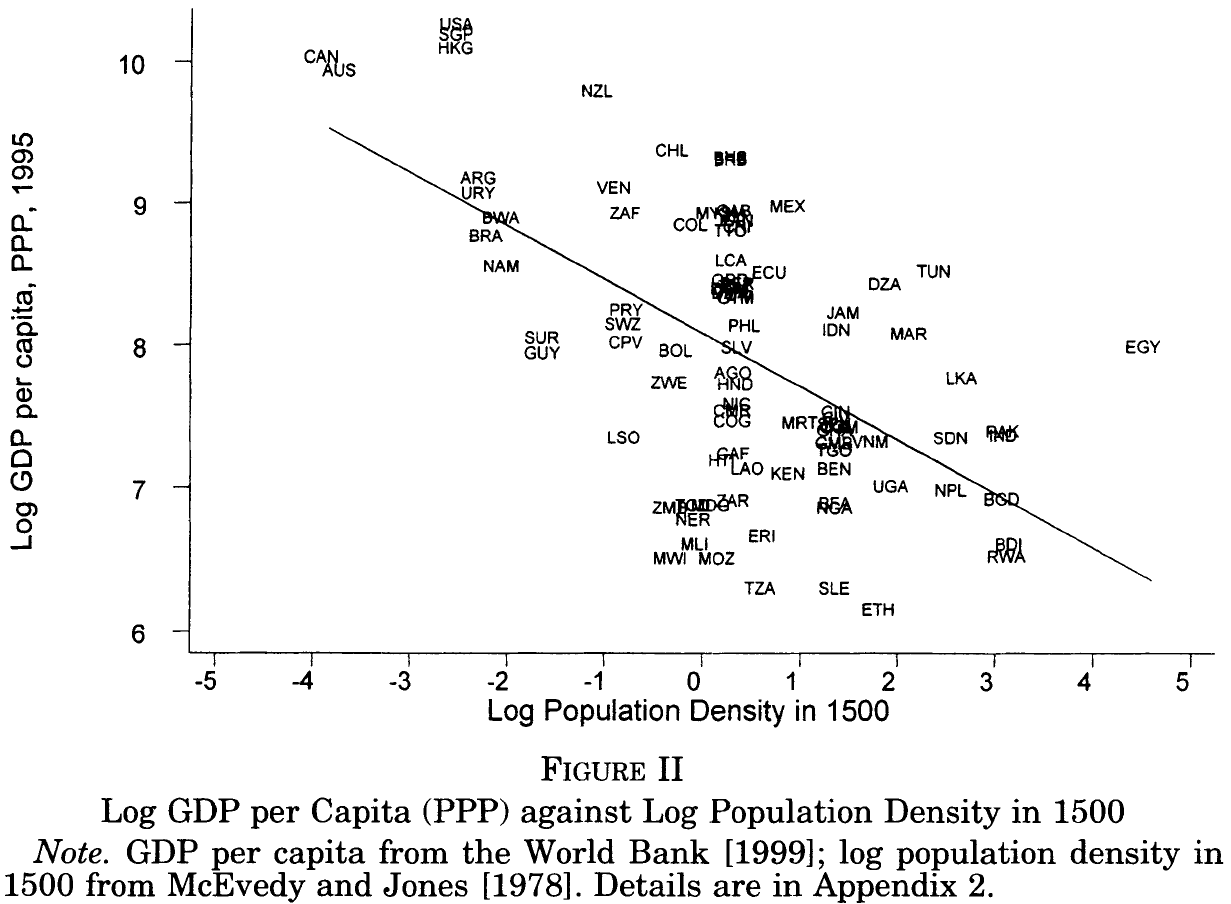
Originally published at joefrancis.info Joe Francis Daron Acemoglu, Simon Johnson and James Robinson (AJR, 2002) famously argued that a ‘reversal of fortune’ had taken place among ex-European colonies. Generally speaking, they argued, those ex-colonies that had been richest in 1500 would become the poorest by the end of the twentieth century. This, they claimed, was […]
Continue ReadingJeffrey Williamson’s Terms of Trade
Originally published at joefrancis.info Joe Francis Jeffrey Williamson‘s (2011) book Trade and Poverty: When the Third World Fell Behind is one of the most interesting attempts to explain the ‘great divergence’ between rich and poor countries. It is a shame, then, that it is marred by his use of Mickey Mouse numbers. In simplified terms, Williamson argues that […]
Continue ReadingFix, ‘Economic Development and the Death of the Free Market’
Abstract According to neoclassical economics, the most efficient way to organize human activity is to use the free market. By stoking self interest, the theory claims, individuals can benefit society. This idea, however, conflicts with the evolutionary theory of multilevel selection, which proposes that rather than stoke individual self interest, successful groups must suppress it. […]
Continue ReadingThe Paradox of Individualism and Hierarchy
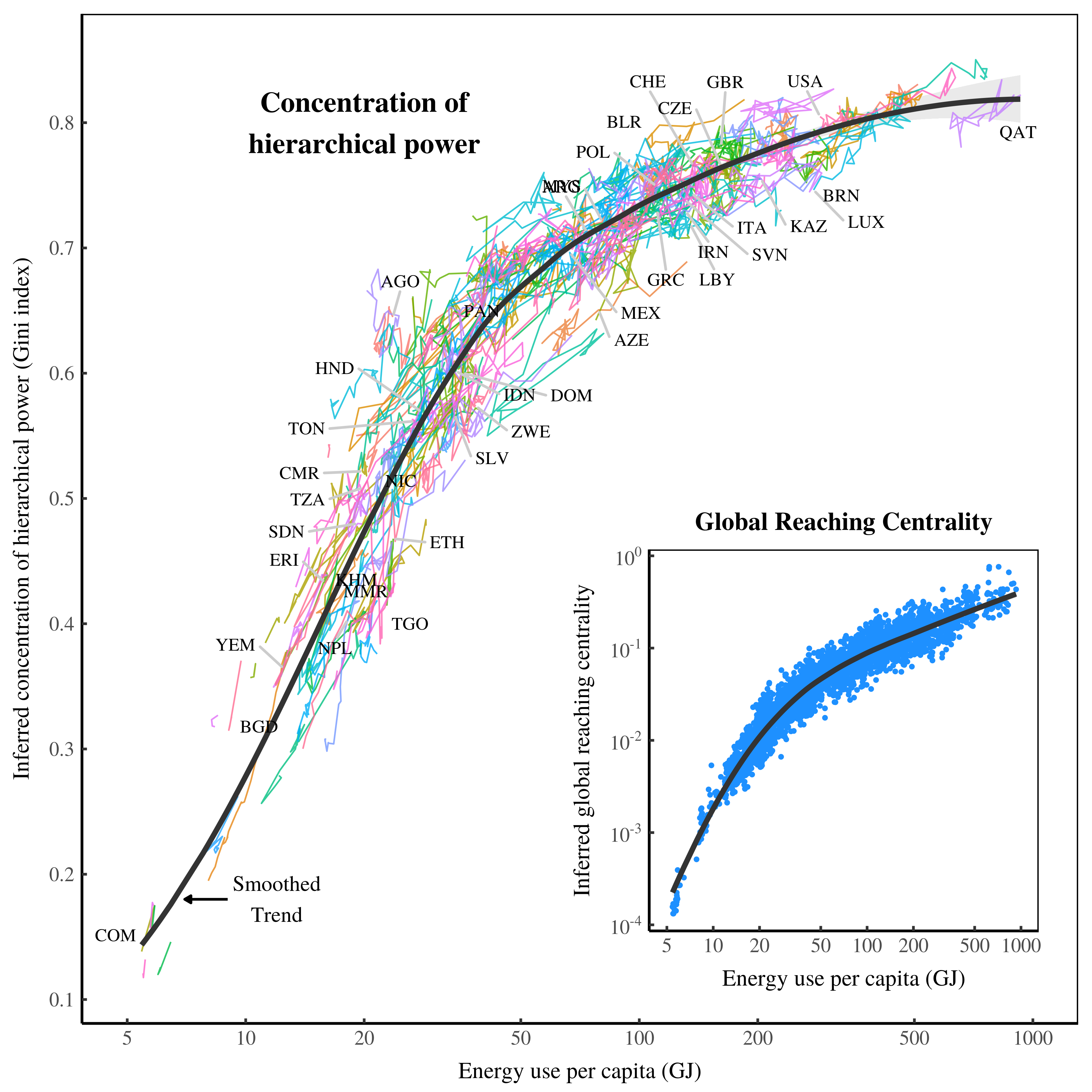
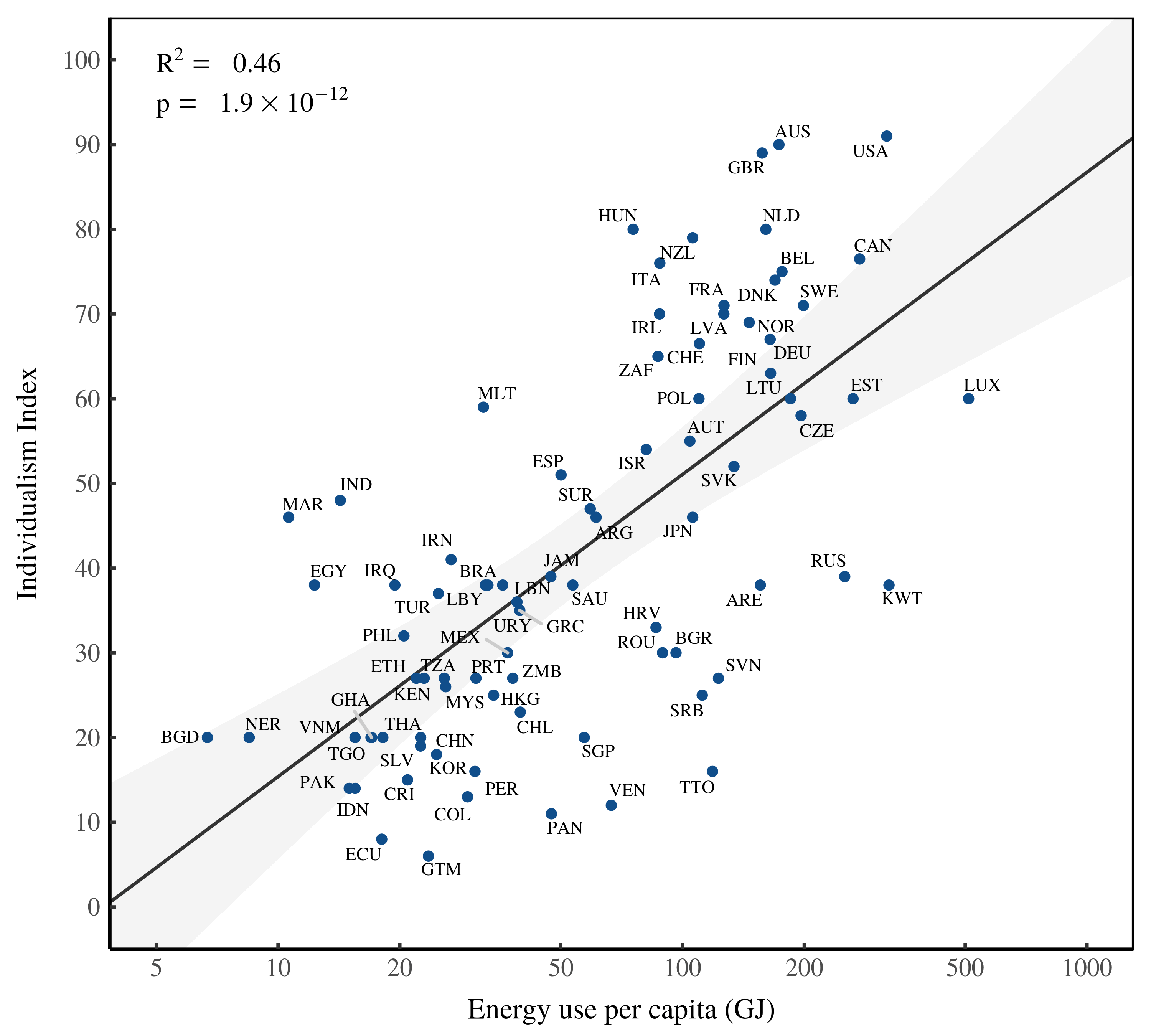
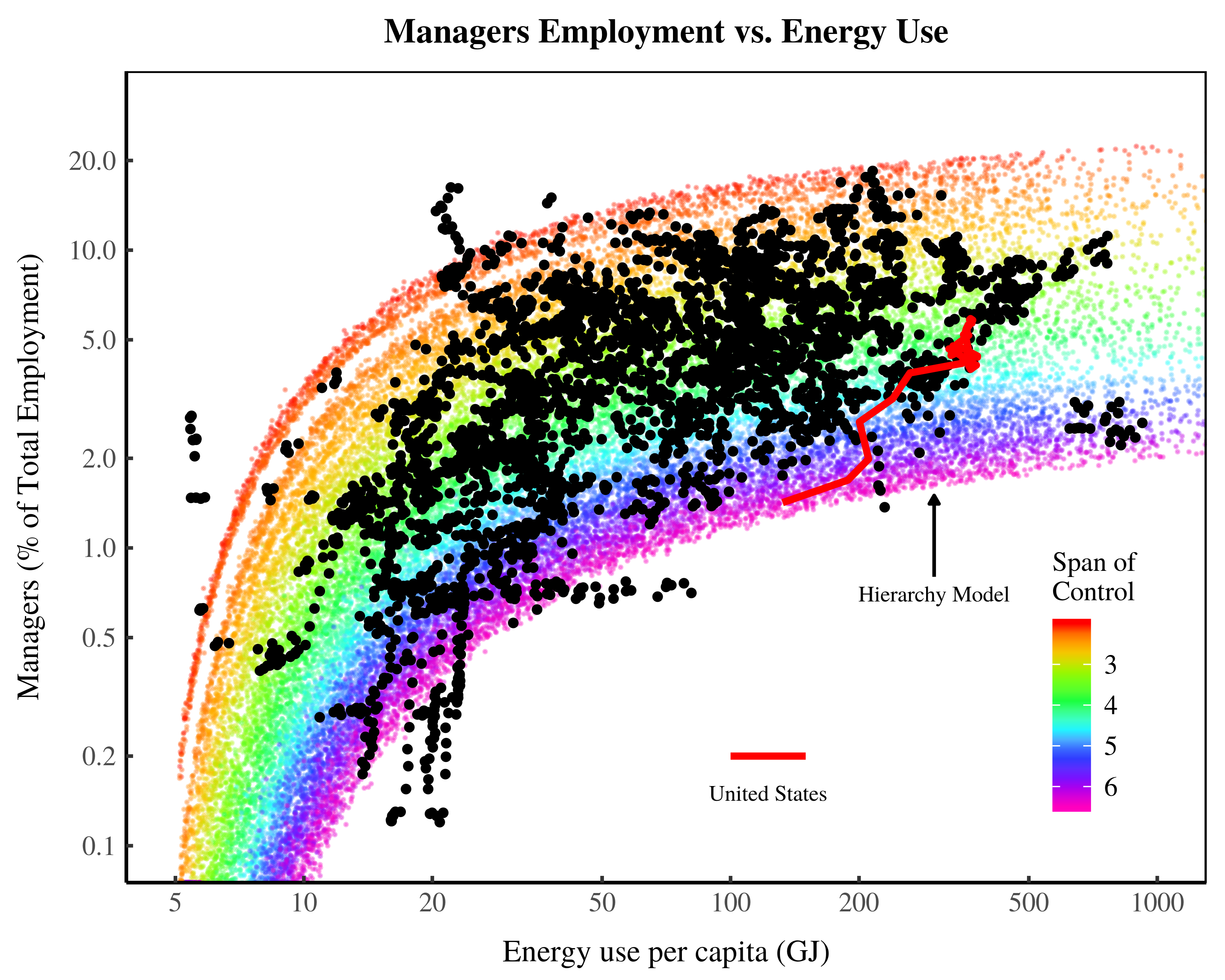
Originally published on Economics from the Top Down Blair Fix In the early 1970s, Geert Hofstede discovered something interesting. While analyzing a work-attitude survey that had been given to thousands of IBM employees around the world, Hofstede found that responses clustered by country. In some countries, for instance, employees tended to prefer an autocratic style […]
Continue Reading2020/01: Fix, ‘Economic Development and the Death of the Free Market’
Abstract Free markets are, according to neoclassical economic theory, the most efficient way of organizing human activity. The claim is that individuals can benefit society by acting only in their self interest. In contrast, the evolutionary theory of multilevel selection proposes that groups must suppress the self interest of individuals. They often do so, the […]
Continue ReadingThe Growth of Hierarchy and the Death of the Free Market
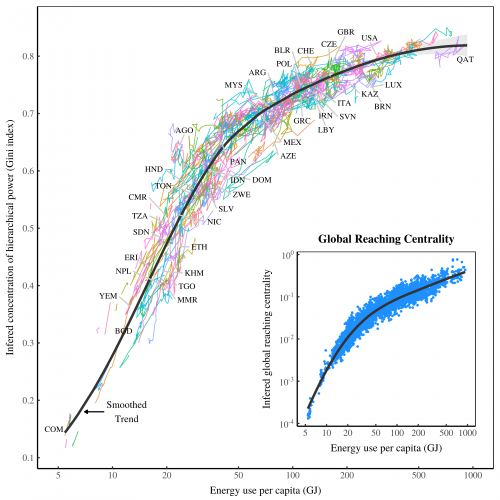
Originally published on Economics from the Top Down Blair Fix Do you believe in free markets? Do you think that unfettered competition is the best way to organize society? If so, this post is intended to shake your faith. No, I’m not going to argue that free markets are bad. Instead, I’m going to show […]
Continue ReadingDi Muzio, ‘The Tragedy of Human Development: A Genealogy of Capital as Power’
Abstract How might an objective observer conceive of what humans have accomplished as a species over its brief history? Benjamin argues that history can be judged as one giant catastrophe. Liberals suggest that this is to sombre an assessment and that human history can be read as a story of greater and greater progress in […]
Continue Reading