Abstract This paper explores how the evolution of human sociality can help us understand how we distribute resources. Using ideas from sociobiology, I argue that resource distribution is marked by a tension between two levels of natural selection. At the group level, selfless behavior is advantageous. But at the individual level, selfish behavior is advantageous. […]
Continue ReadingFix, ‘Personal Income and Hierarchical Power’
Abstract This article examines the relation between personal income and hierarchical power. In the context of a firm hierarchy, I define hierarchical power as the number of subordinates under an individual’s control. Using the available case-study evidence, I find that relative income within firms scales strongly with hierarchical power. I also find that hierarchical power […]
Continue ReadingAre We Measuring Inequality the Wrong Way?
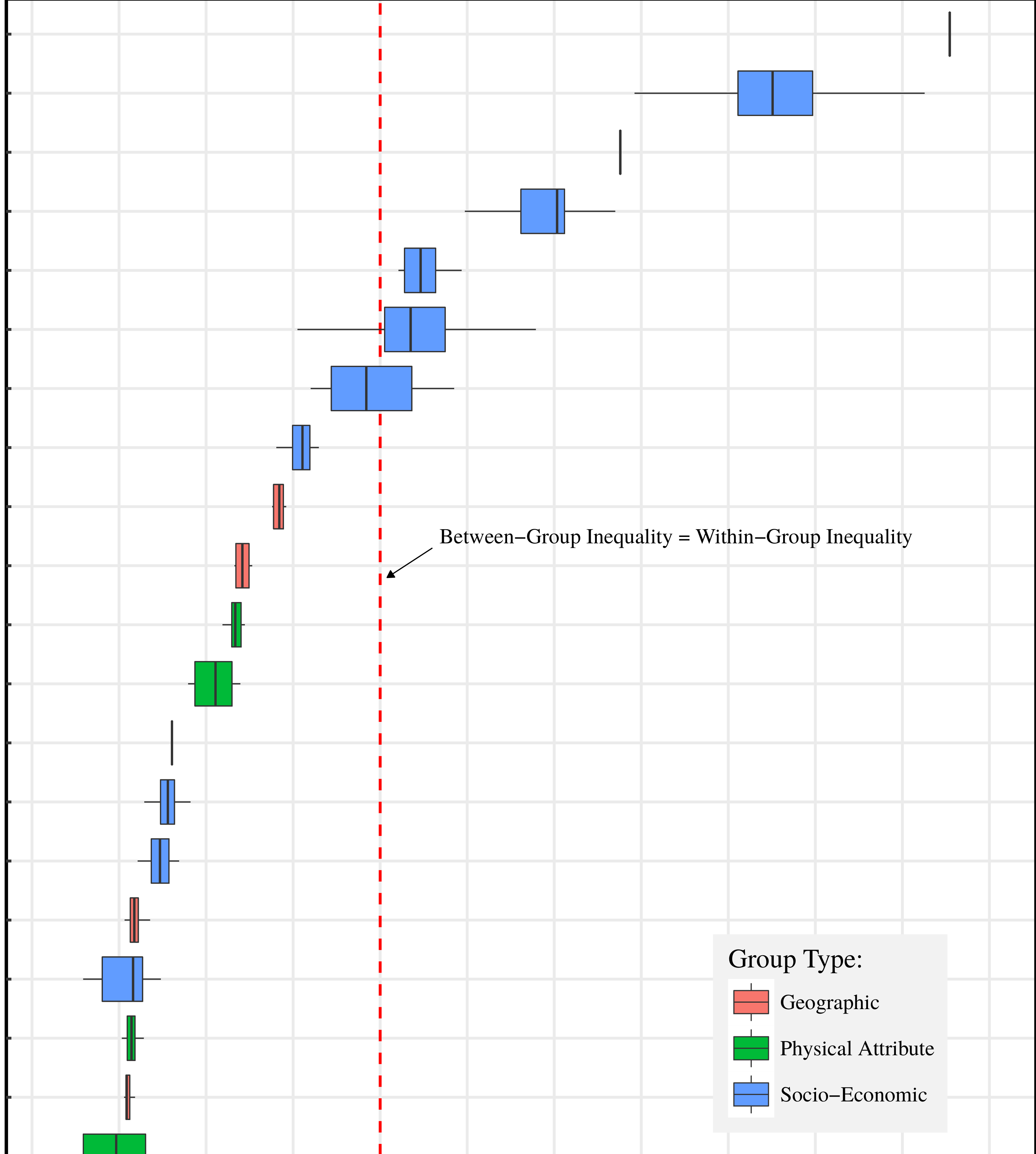
Originally published on Economics from the Top Down Blair Fix In a recent blog post called “How Not to Measure Inequality”, the anthropologist Jason Hickel argues that economists measure inequality the wrong way. Hickel thinks that standard measures of inequality (such as the Gini index), underestimate global disparities. The problem, according to Hickel, is that […]
Continue ReadingThe Allure of Marxism … And Why It’s a Mistake
Originally published on Economics from the Top Down Blair Fix Karl Marx is probably the most important social scientist in history. But while his influence is beyond compare, Marx’s legacy is, in many ways, disastrous. Few thinkers have inspired so many people to commit crimes against humanity. Think of Stalinist gulags. Think of the Ukrainian […]
Continue ReadingAs it Dies, We Talk About the ‘Free Market’ More
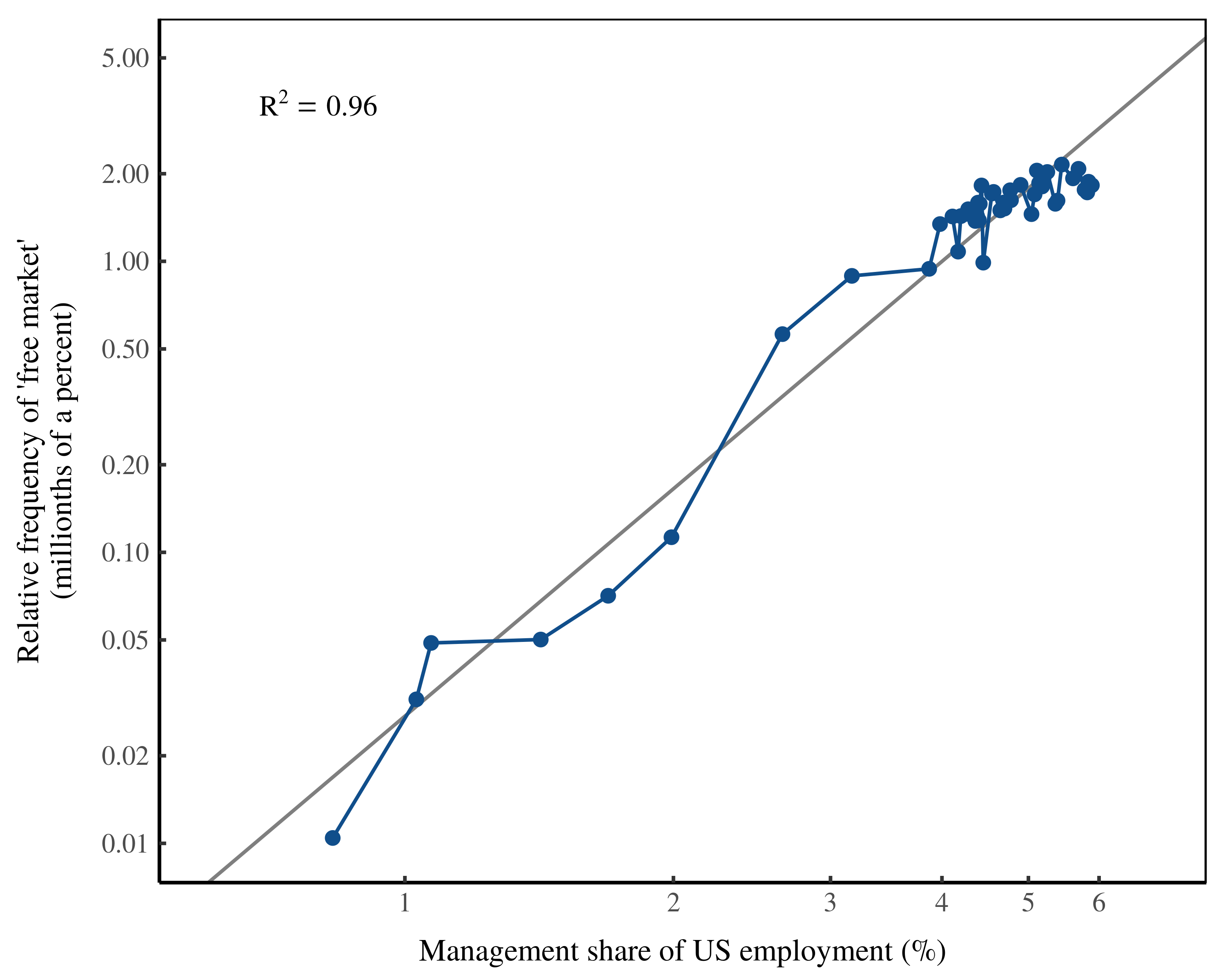
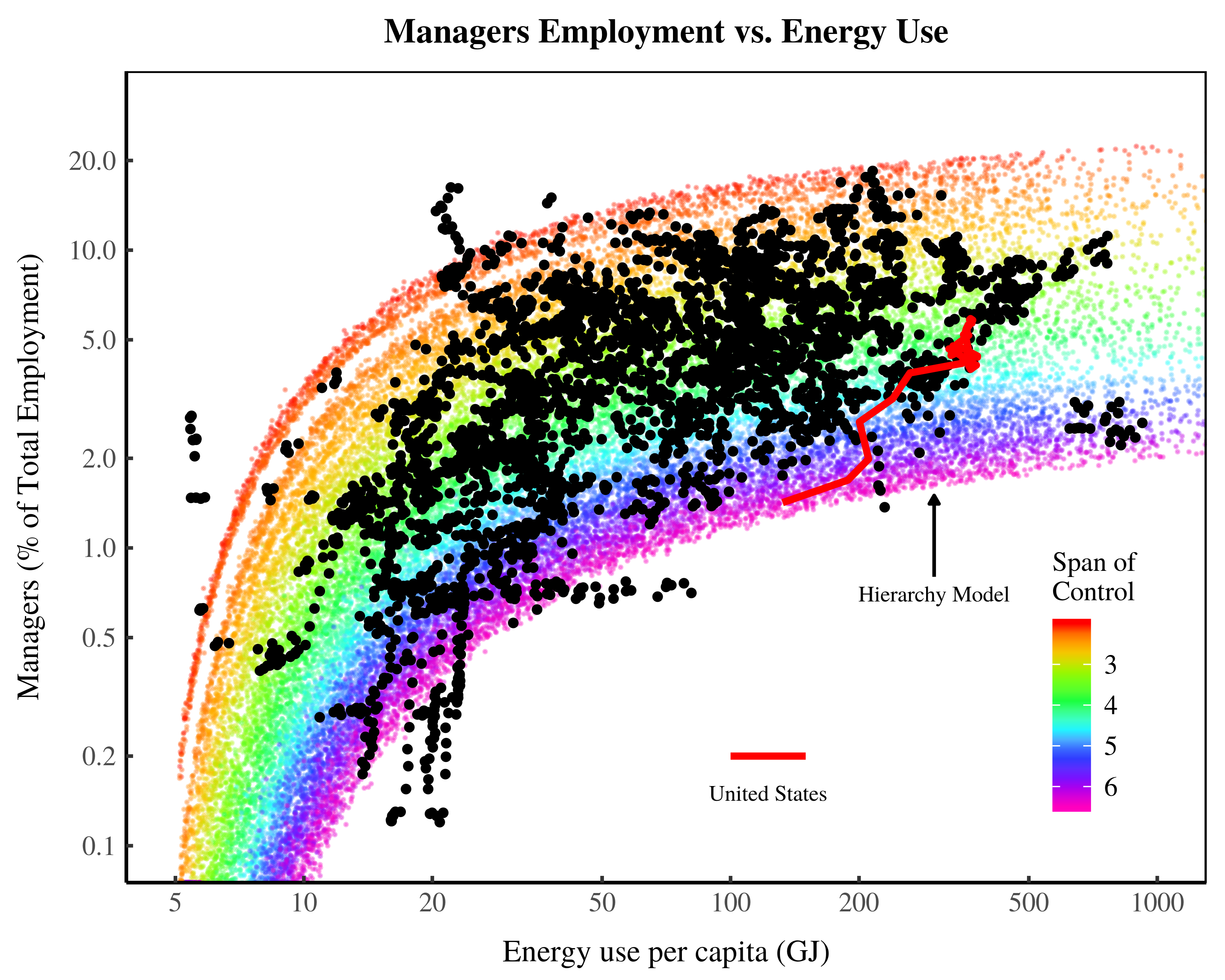
Originally published on Economics from the Top Down Blair Fix In The Growth of Hierarchy and the Death of the Free Market, I argued that economic development involves killing the free market. What was the evidence? As energy use increases, so does the relative number of managers. This growth of managers, I argued, indicates that […]
Continue ReadingCan A Service Transition Save the Planet?
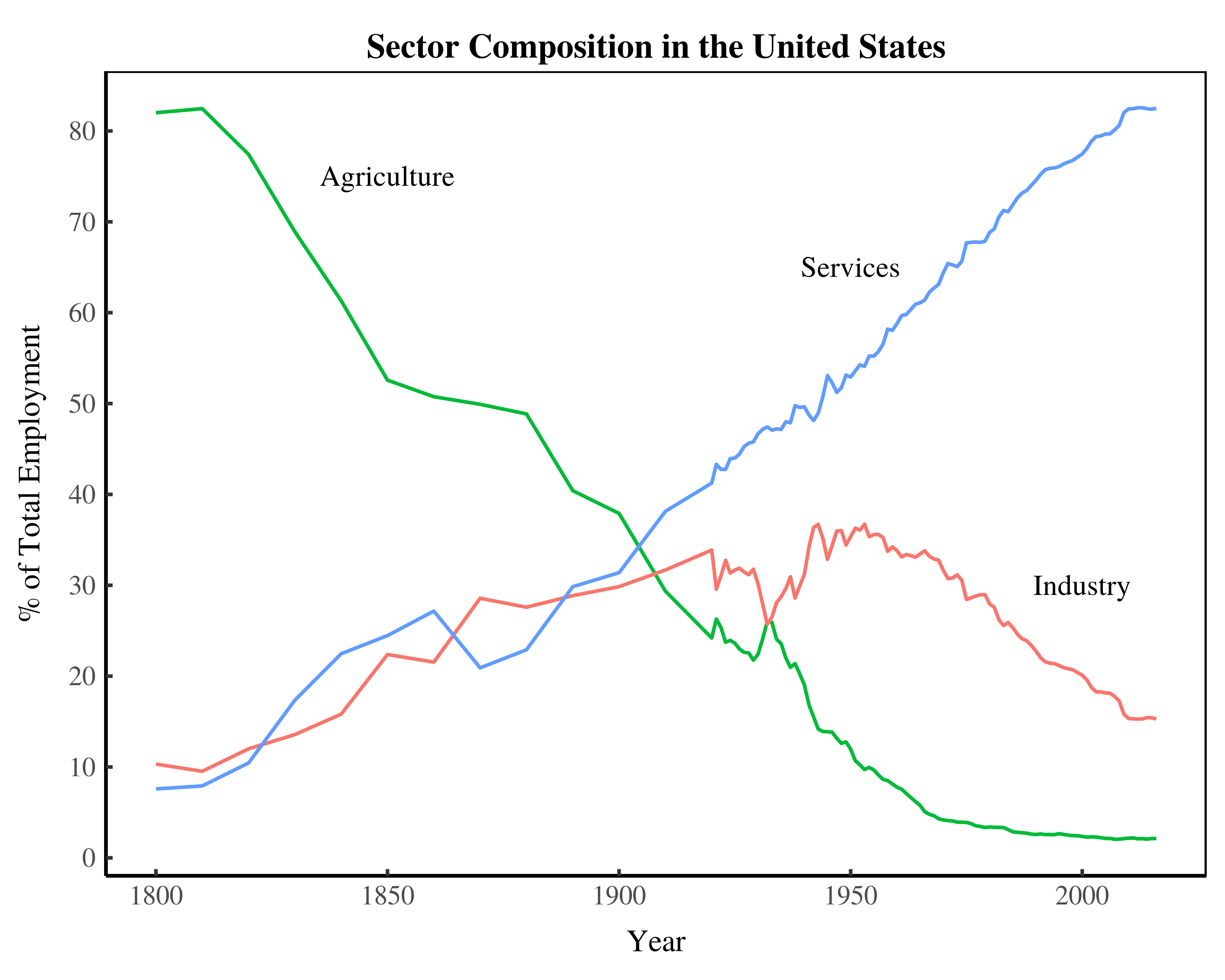
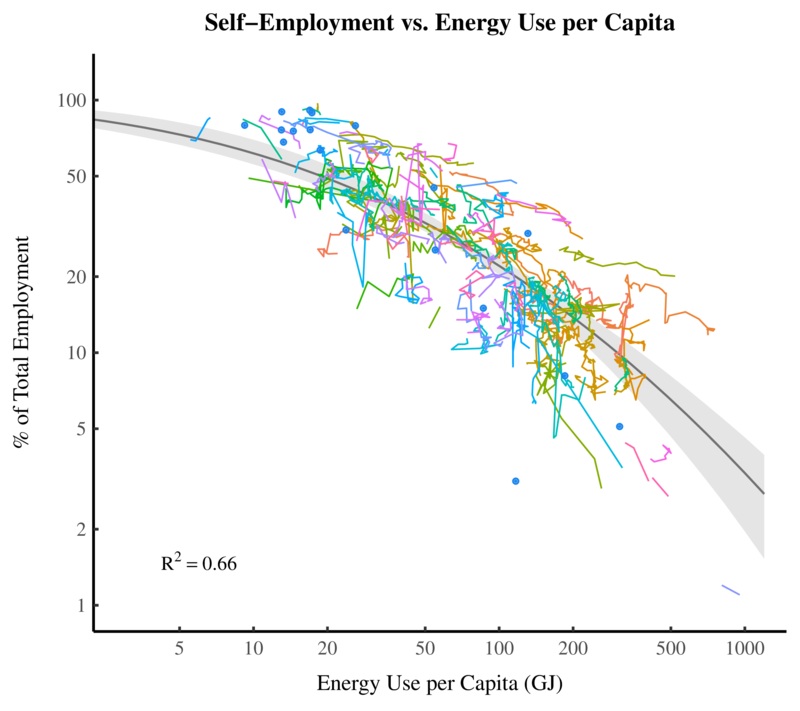
Originally published on Economics from the Top Down Blair Fix Let’s talk sustainability. Unless you’re an anti-science crank, you probably agree that we’ve got a problem with carbon emissions. We need to drastically cut emissions to avoid catastrophic climate change. On this we should all agree. The question that’s open for debate is how to […]
Continue ReadingWhere’s the Barefoot Revolution in Economics?
Originally published on Economics from the Top Down Blair Fix Yesterday I was reminded of what got me interested in economics. I’ll preface this by saying that I make my living as a substitute teacher in Toronto. It’s not glamorous, but it pays the bills. It gives me time to do research from outside academia. […]
Continue ReadingDow, ‘Canada’s Carbon Capitalism: In the Age of Climate Change’
Abstract This historically and critically informed dissertation investigates the question why Canada has become one of the world’s leaders in promoting fossil fuels through its unconventional hydrocarbon industry in spite of the science and growing awareness of climate change. Using a critical historical political economy approach that encompasses both ecological or biophysical scientific realities and […]
Continue ReadingThe Growth of Hierarchy and the Death of the Free Market
Originally published on Economics from the Top Down Blair Fix Do you believe in free markets? Do you think that unfettered competition is the best way to organize society? If so, this post is intended to shake your faith. No, I’m not going to argue that free markets are bad. Instead, I’m going to show […]
Continue ReadingEnergy and the Size Distribution of Firms
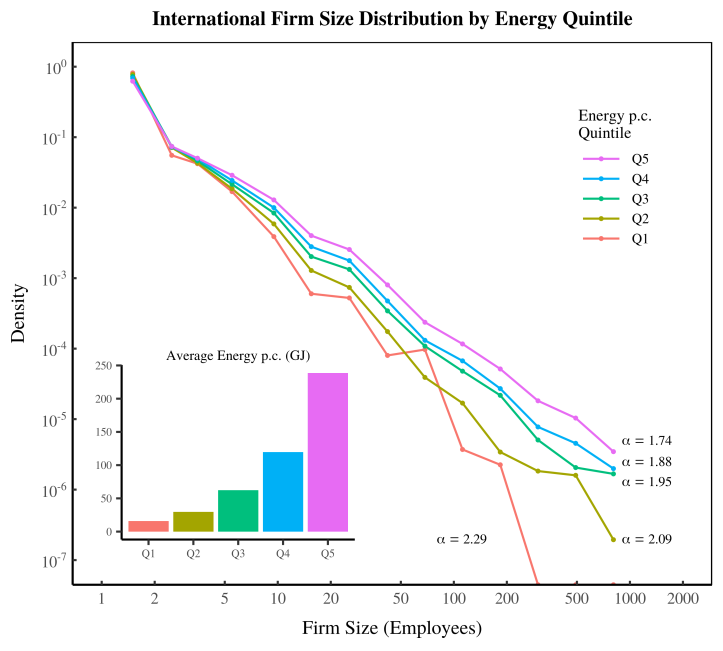
Originally published on Economics from the Top Down Blair Fix In this post, I’m going to return to the relation between energy and institution size. When we left off last time (in Groping in the Dark), I had described my struggle to understand how the size of firms and governments changes with energy use. It […]
Continue ReadingVisualizing Power-Law Distributions
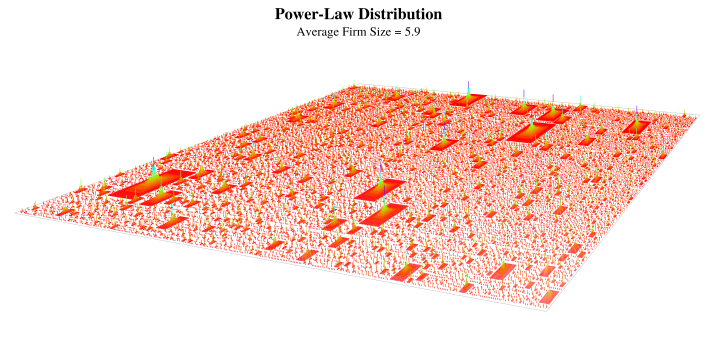
Originally published on Economics from the Top Down Blair Fix In this post we’re going to take a journey into the world of power-law distributions. Power laws pop up again and again in my research. But I’ve never taken the time to discuss what makes them so weird. This post will be a little ‘power-law […]
Continue ReadingThe Autocatalytic Sprawl of Pseudorational Mastery
The Autocatalytic Sprawl of Pseudorational Mastery ULF MARTIN May 2019 Abstract According to Jonathan Nitzan and Shimshon Bichler (2009), capital is not an economic quantity, but a mode of power. Their fundamental thesis could be summarized as follows: capital is power quantified in monetary terms. But what do we do when we quantify? What is […]
Continue ReadingAgent-Based Models and the Ghost in the Machine
Originally published on Economics from the Top Down Blair Fix In the opening post of this blog, I described my ‘top-down’ approach to studying society. This means studying groups of people without trying to reduce everything to the actions of individuals. It’s not that I think individual actions are unimportant. Of course they are important. […]
Continue ReadingGroping in the Dark: The Untold Side of Research
Originally published on Economics from the Top Down Blair Fix There is an exciting side of blogging that I want to explore here. Blogging can tell the story behind research. This is something you don’t get in journals. Most scientific articles obey a formula that goes like this: Here is the question I asked. Here […]
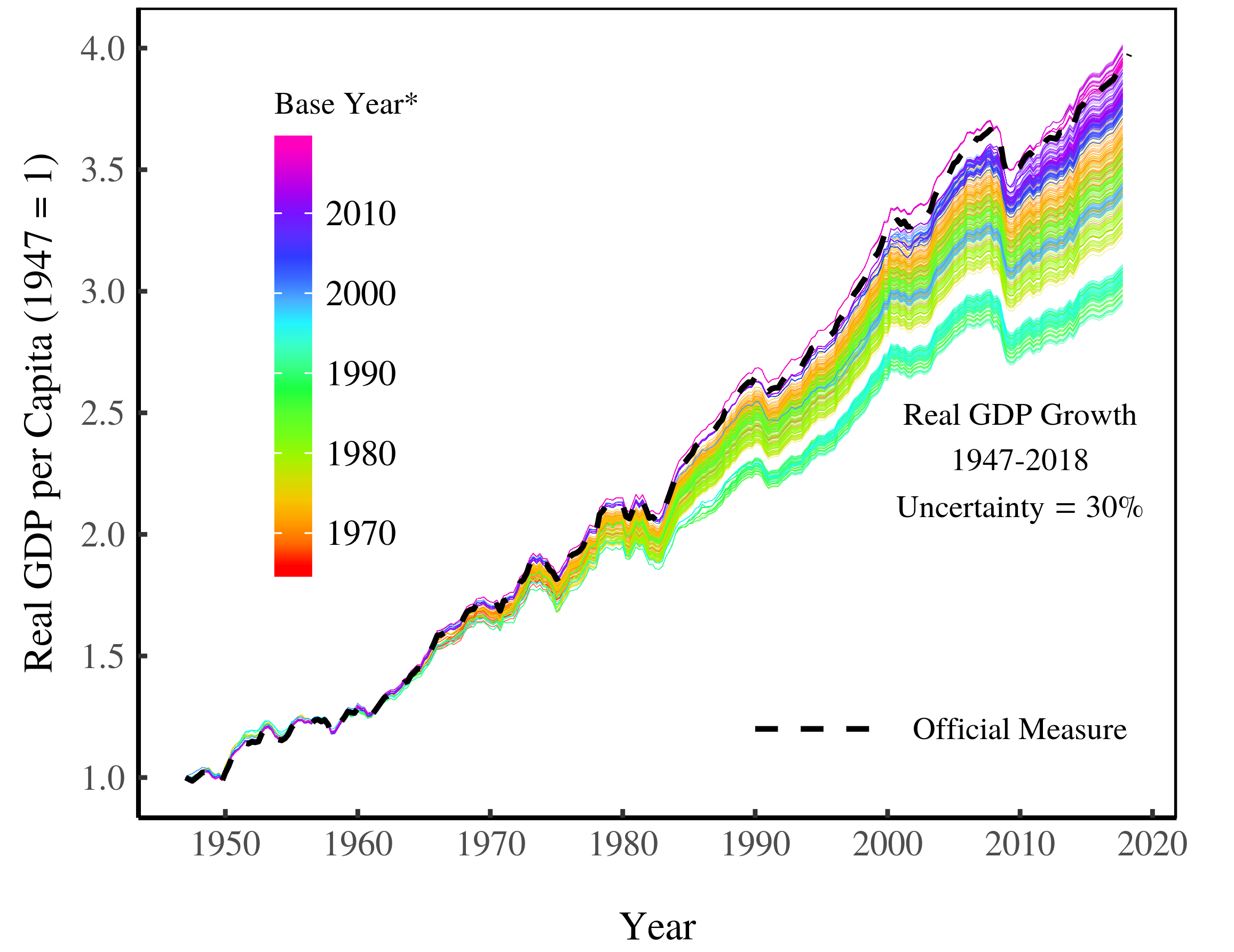
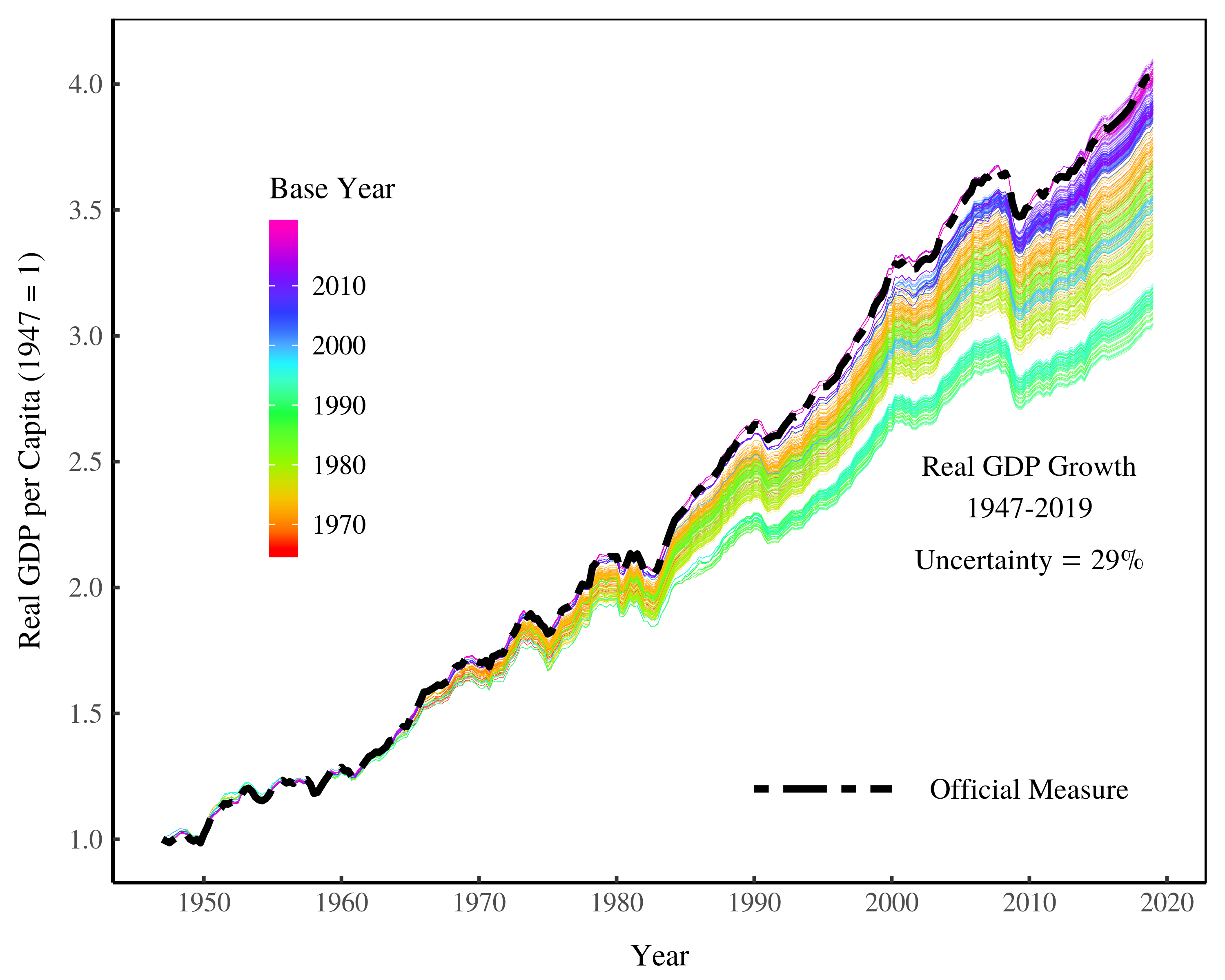
Continue ReadingReal GDP: The Flawed Metric at the Heart of Macroeconomics
Blair Fix, Jonathan Nitzan and Shimshon Bichler The study of economic growth is central to macroeconomics. More than anything else, macroeconomists are concerned with finding policies that encourage growth. And by ‘growth’, they mean the growth of real GDP. This measure has become so central to macroeconomics that few economists question its validity. Our intention […]
Continue ReadingFix, ‘Energy, Hierarchy and the Origin of Inequality’
Abstract Where should we look to understand the origin of inequality? I propose an unusual window of evidence — modern societies. I hypothesize that evidence for the origin of inequality is encoded in the institutional structure of industrial societies. To test this idea, I use a model to project modern trends into the past. This […]
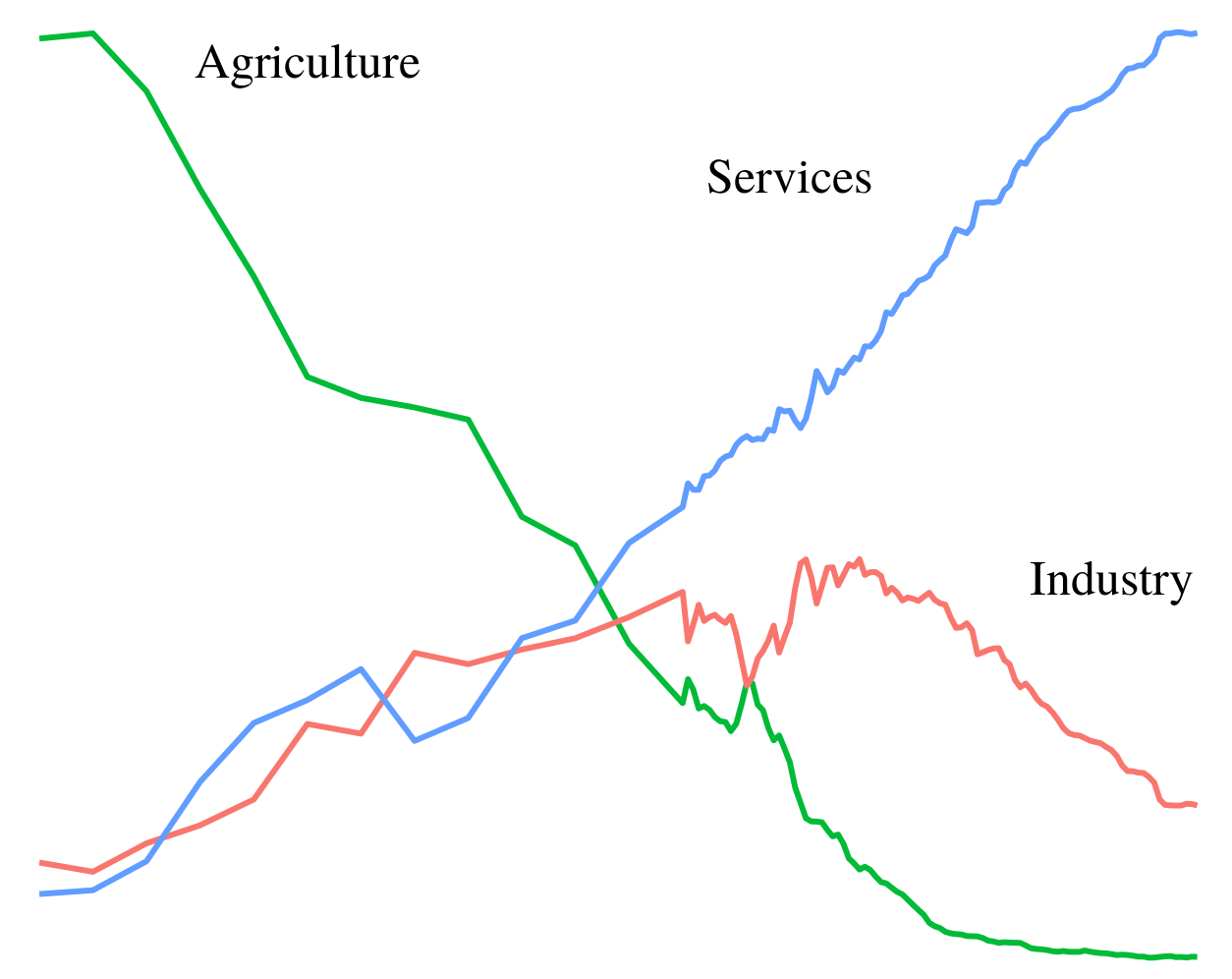
Continue ReadingFix, ‘Dematerialization Through Services: Evaluating the Evidence’
Abstract Dematerialization through services is a popular proposal for reducing environmental impact. The idea is that by shifting from the production of goods to the provision of services, a society can reduce its material demands. But do societies with a larger service sector actually dematerialize? I test the ‘dematerialization through services’ hypothesis with a focus […]
Continue ReadingFix, ‘The Aggregation Problem: Implications for Ecological and Biophysical Economics’
Abstract This paper discusses the dimension problem in economic aggregation, as it relates to ecological and biophysical economics. The dimension problem consists of a simple dilemma: when we aggregate, the observer must choose the dimension of analysis. The dilemma is that this choice affects the resulting measurement. This means that aggregate measurements are dependent on […]
Continue ReadingFix, ‘The Trouble With Human Capital Theory’
Abstract Human capital theory is the dominant approach for understanding personal income distribution. According to this theory, individual income is the result of ‘human capital’. The idea is that human capital makes people more productive, which leads to higher income. But is this really the case? This paper takes a critical look at human capital […]
Continue ReadingPropertization: The Process by which Financial Corporate Power has Risen and Collapsed
Propertization The Process by which Financial Corporate Power has Risen and Collapsed JONGCHUL KIM September 2018 Abstract Elsewhere I argue that the legal concept of property was created in the image of money in the late Roman Republic. Since then, the division of property and contract has been an underlying structure of Western law. The […]
Continue Reading