Abstract There is little doubt that, in the last hundred years or so, progress has been made in lifting more people out of extreme poverty. Yet, considerable economic inequalities both within and between nations persists and, as recent work has shown, if the rate of return on capital surpasses the rate of growth, inherited wealth […]
Continue ReadingEnergizing Exchange: Learning from Econophysics’ Mistakes
Originally published at Economics from the Top Down Blair Fix Let’s talk econophysics. If you’re not familiar, ‘econophysics’ is an attempt to understand economic phenomena (like the distribution of income) using the tools of statistical mechanics. The field has been around for a few decades, but has received little attention from mainstream economists. I think […]
Continue ReadingRadically Progressive Degrowth: Reducing Resource Use by Eliminating Inequality
Originally published at Economics from the Top Down Blair Fix Pity the billionaires. High in the towers on Billionaires’ Row, life is hard. The pencil-thin buildings groan as they sway in the wind, keeping penthouse dwellers up at night. Water pipes break, ruining posh décor. And elevators are unreliable, interrupting billionaires’ highly productive lives. So […]
Continue ReadingFix, ‘Redistributing Income Through Hierarchy’
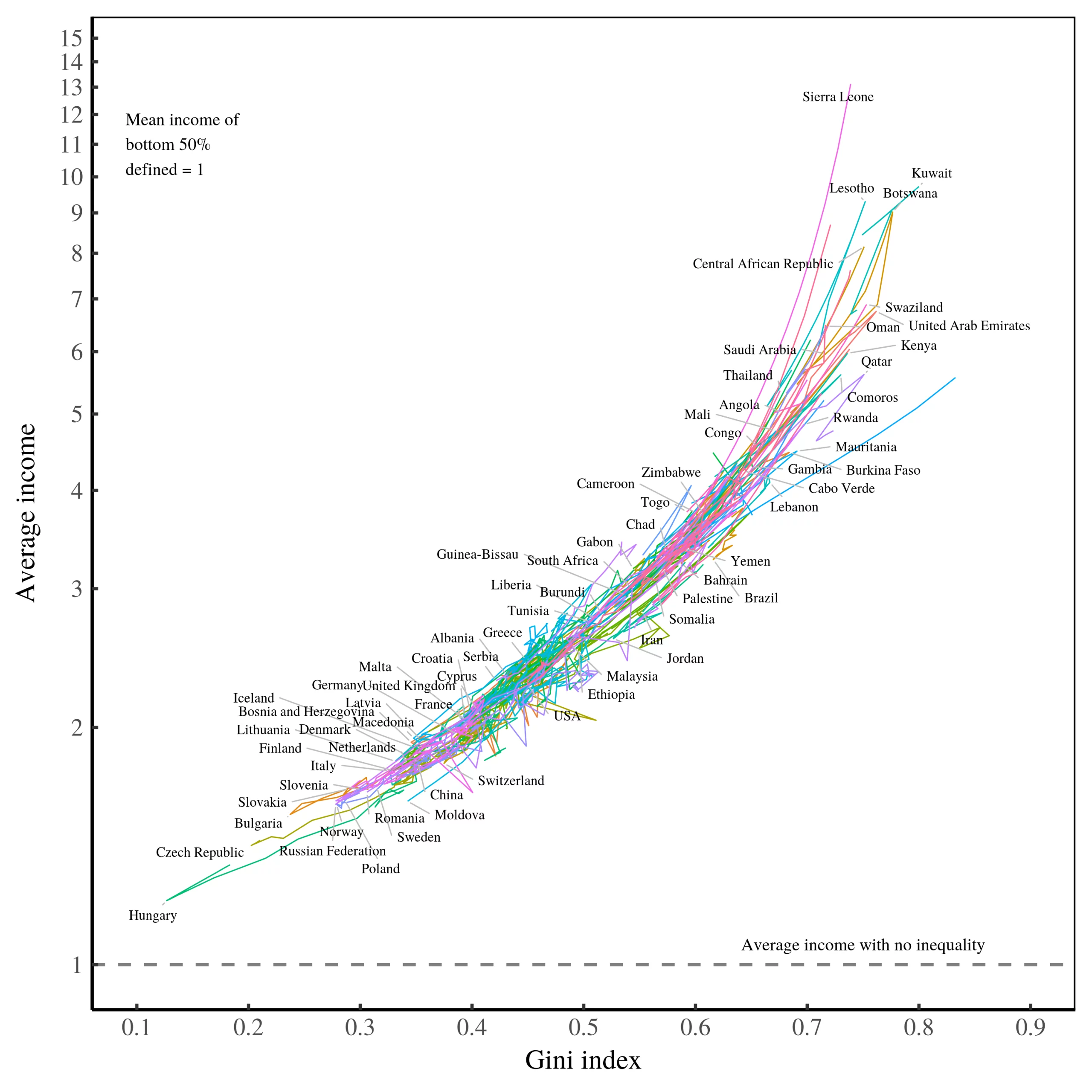
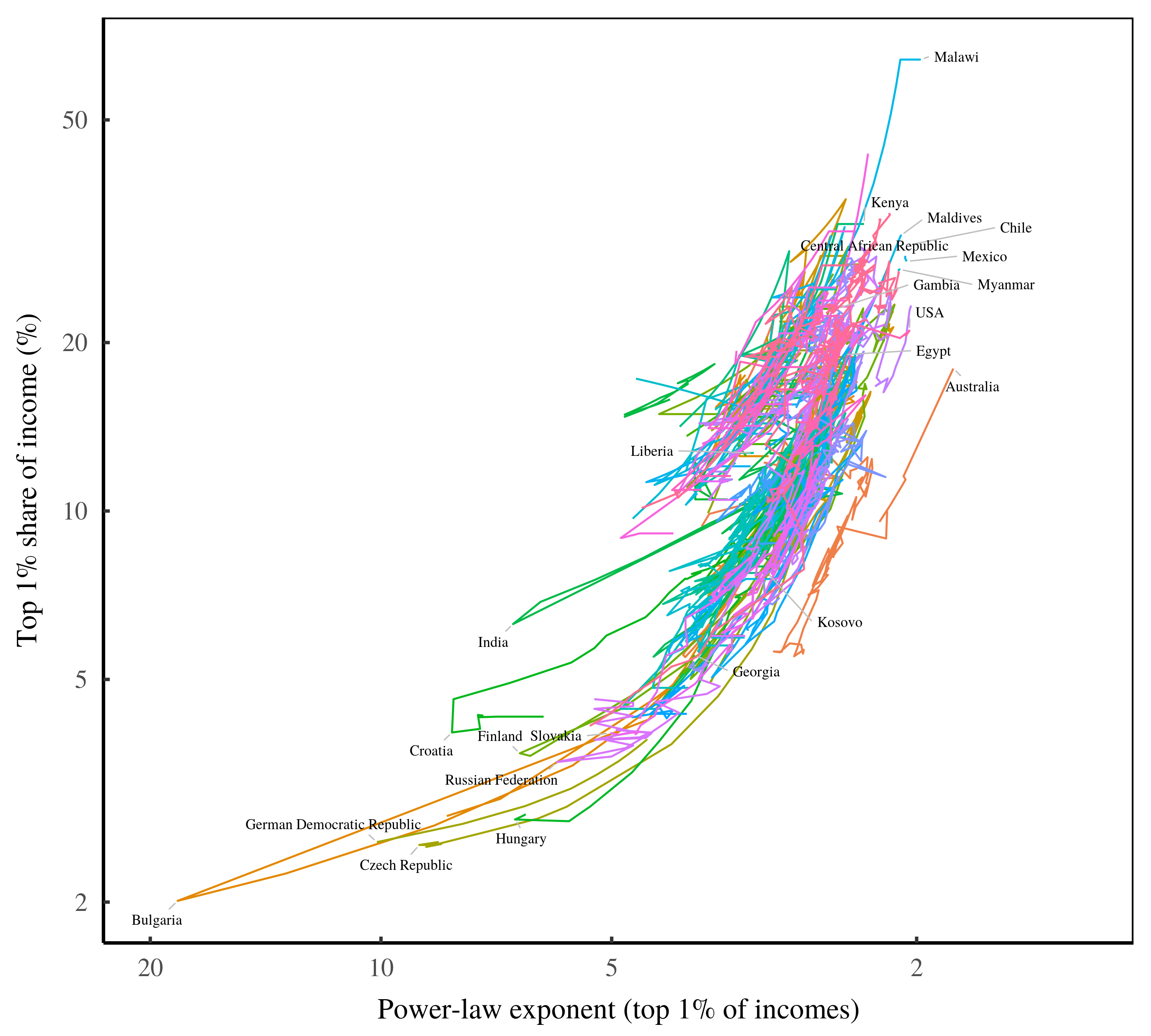
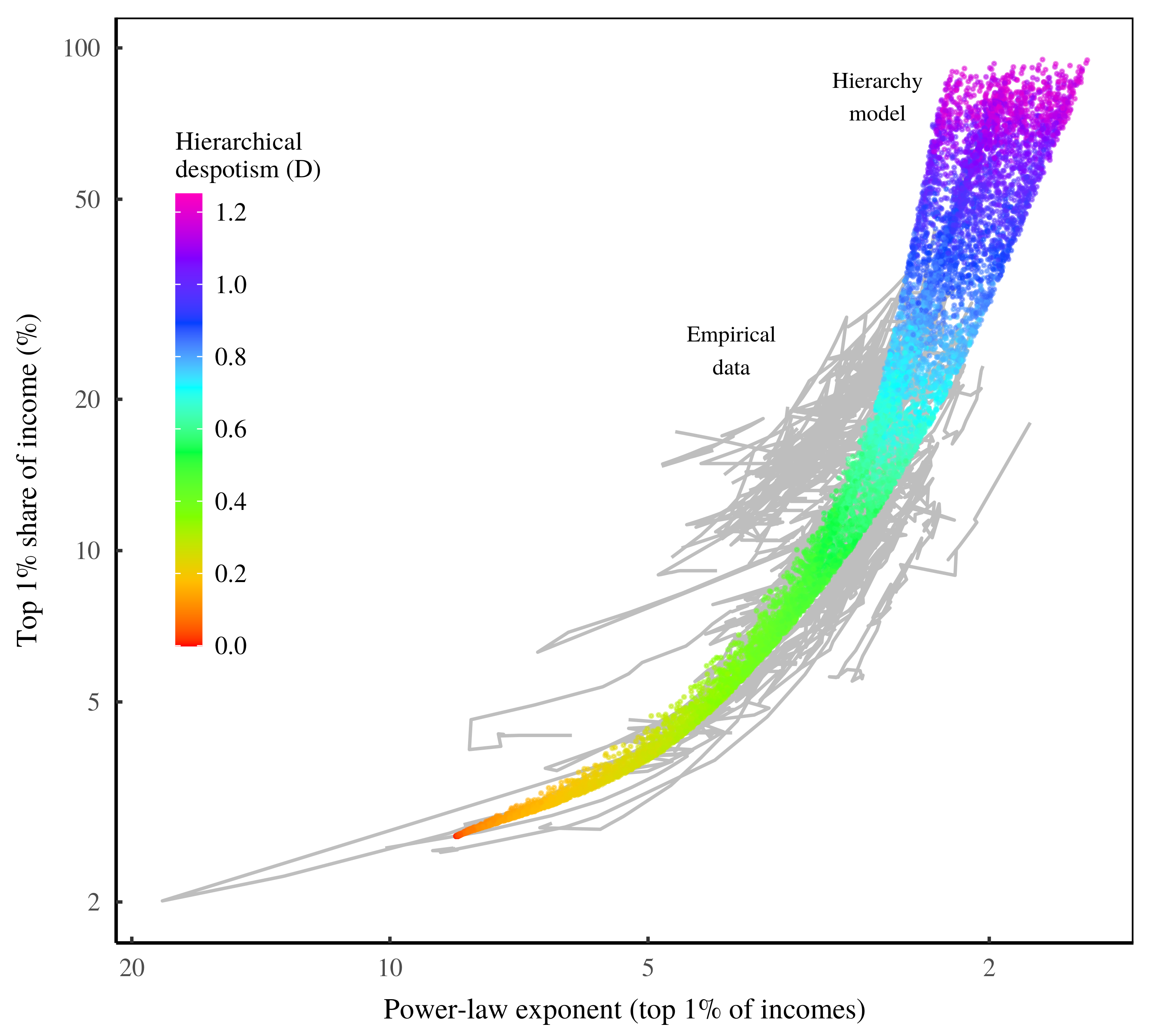
Abstract Although the determinants of income are complex, the results are surprisingly uniform. To a first approximation, top incomes follow a power-law distribution, and the redistribution of income corresponds to a change in the power-law exponent. Given the messiness of the struggle for resources, why is the outcome so simple? This paper explores the idea […]
Continue ReadingThe ideology of economics
Originally published at pluralistic.net Cory Doctorow Thomas Piketty’s “Capital in the 21st Century” advanced a simple, data-supported hypothesis: that markets left to their own will cause capital to grow faster than the economy as a whole, so over time, the rich always get richer. https://boingboing.net/2014/06/24/thomas-pikettys-capital-in-t.html He’s followed up Capital with the 1000-page “Capital and Ideology” […]
Continue Reading2021/04: Fix, ‘Redistributing Income Through Hierarchy’
Abstract Although the determinants of income are complex, the results are surprisingly uniform. To a first approximation, top incomes follow a power-law distribution, and the redistribution of income corresponds to a change in the power-law exponent. Given the messiness of the struggle for resources, why is the outcome so simple? This paper explores the idea […]
Continue ReadingInequality Looks Very Different in Denmark and the US. Why?
Originally published at sbhager.com Sandy Brian Hager The following piece is based on my State of the Art article in Socio-Economic Review. It was originally published for The Conversation and the World Economic Forum Global Agenda. A Spanish translation can be found here. Why do the richest 1% of Americans take 20% of national income, […]
Continue Reading2021/02: Fix, ‘Living the good life in a non-growth world: Investigating the role of hierarchy’
Abstract Humanity’s most pressing need is to learn how to live within our planet’s boundaries — something that likely means doing without economic growth. How, then, can we create a non-growth society that is both just and equitable? I attempt to address this question by looking at an aspect of sustainability (and equity) that is […]
Continue Reading2020/06: Bichler & Nitzan, ‘The Limits of Capitalized Power. A 2020 U.S. Update’
Abstract Until the late 2000s, our work focused primarily on why capitalism should be understood as a mode of power. We argued that capital itself is a form of organized power and researched how capitalists sustain, defend and augment their capitalized power. We called our approach ‘capital as power’ – or CasP, for short. But […]
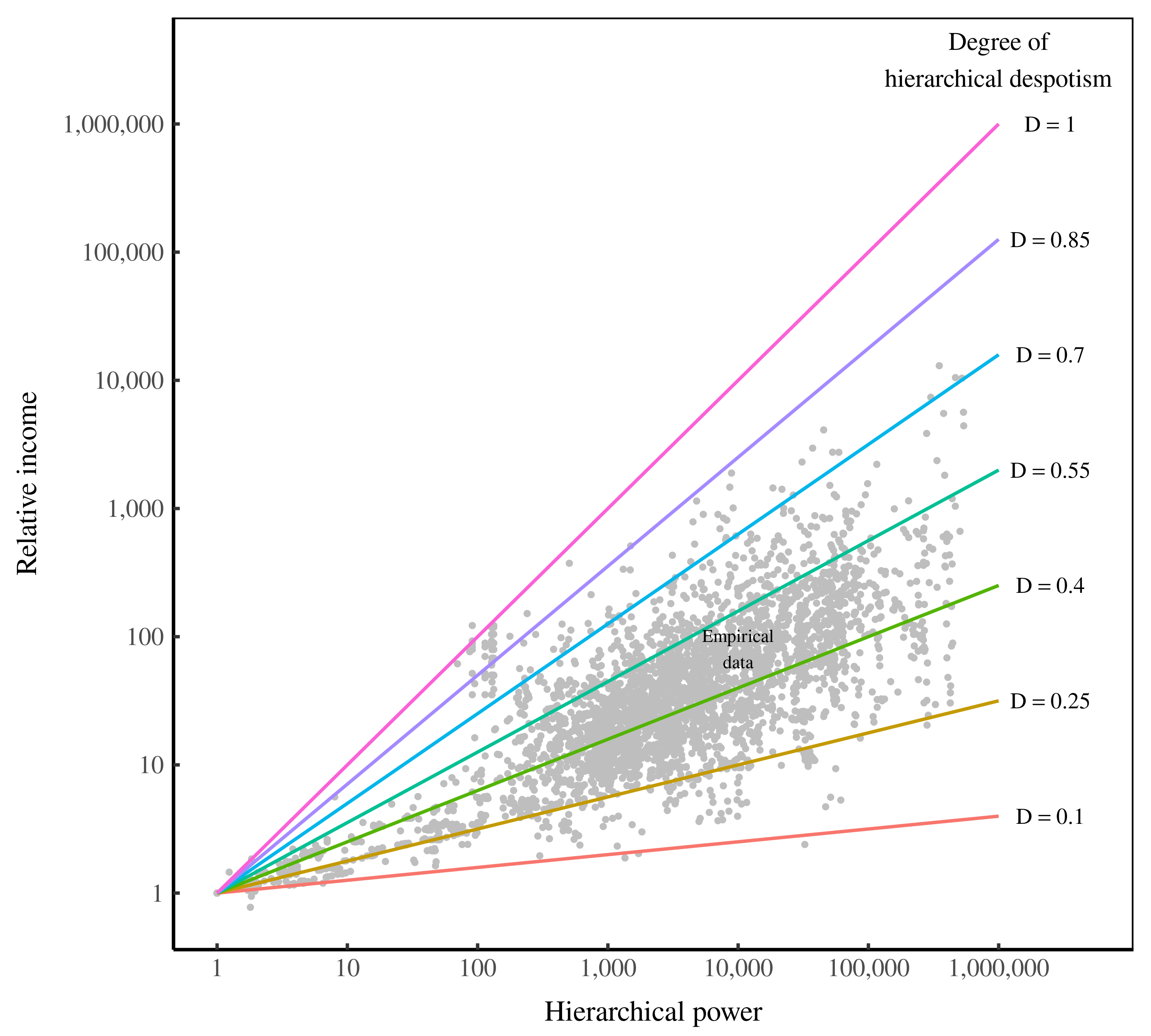
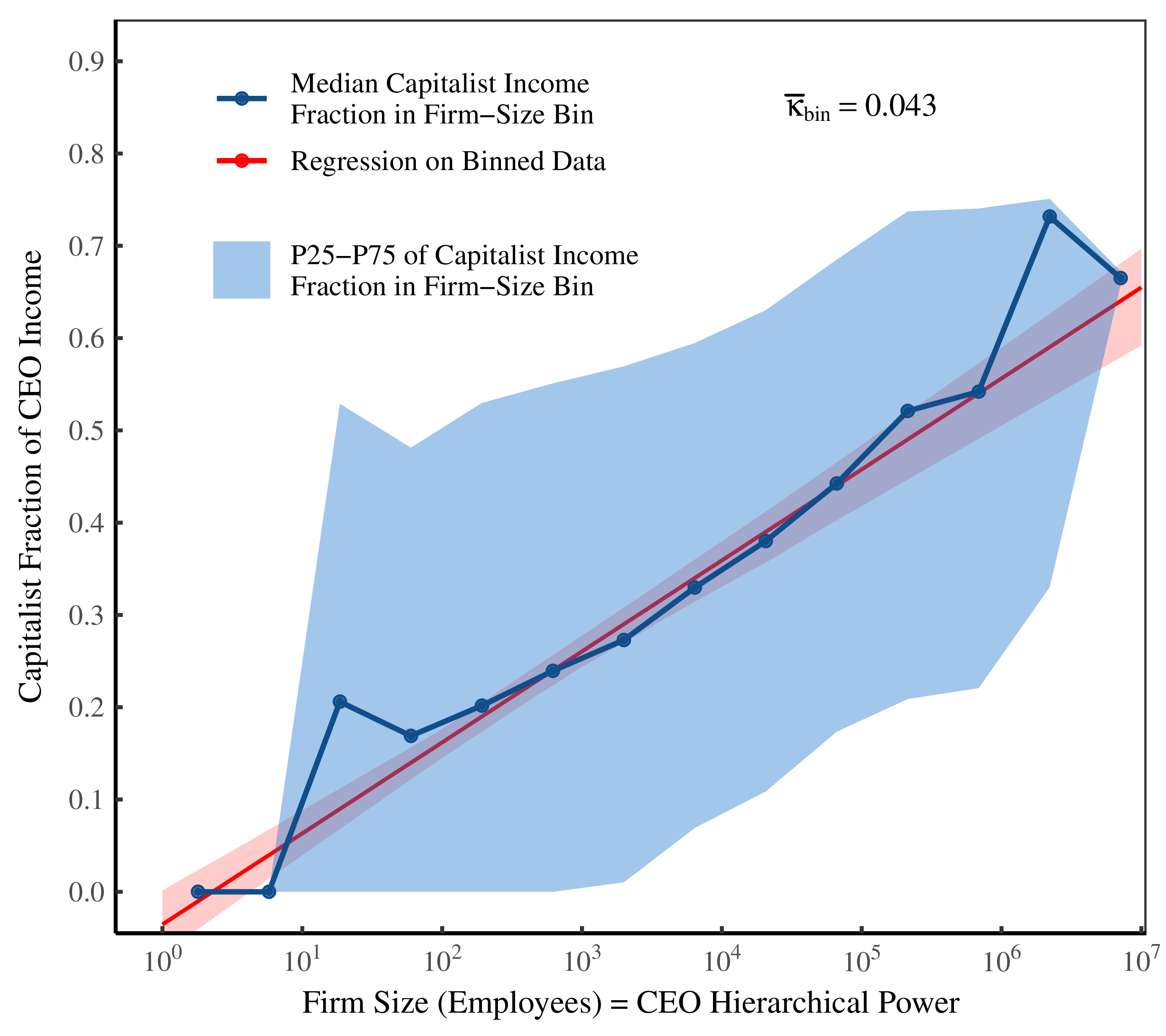
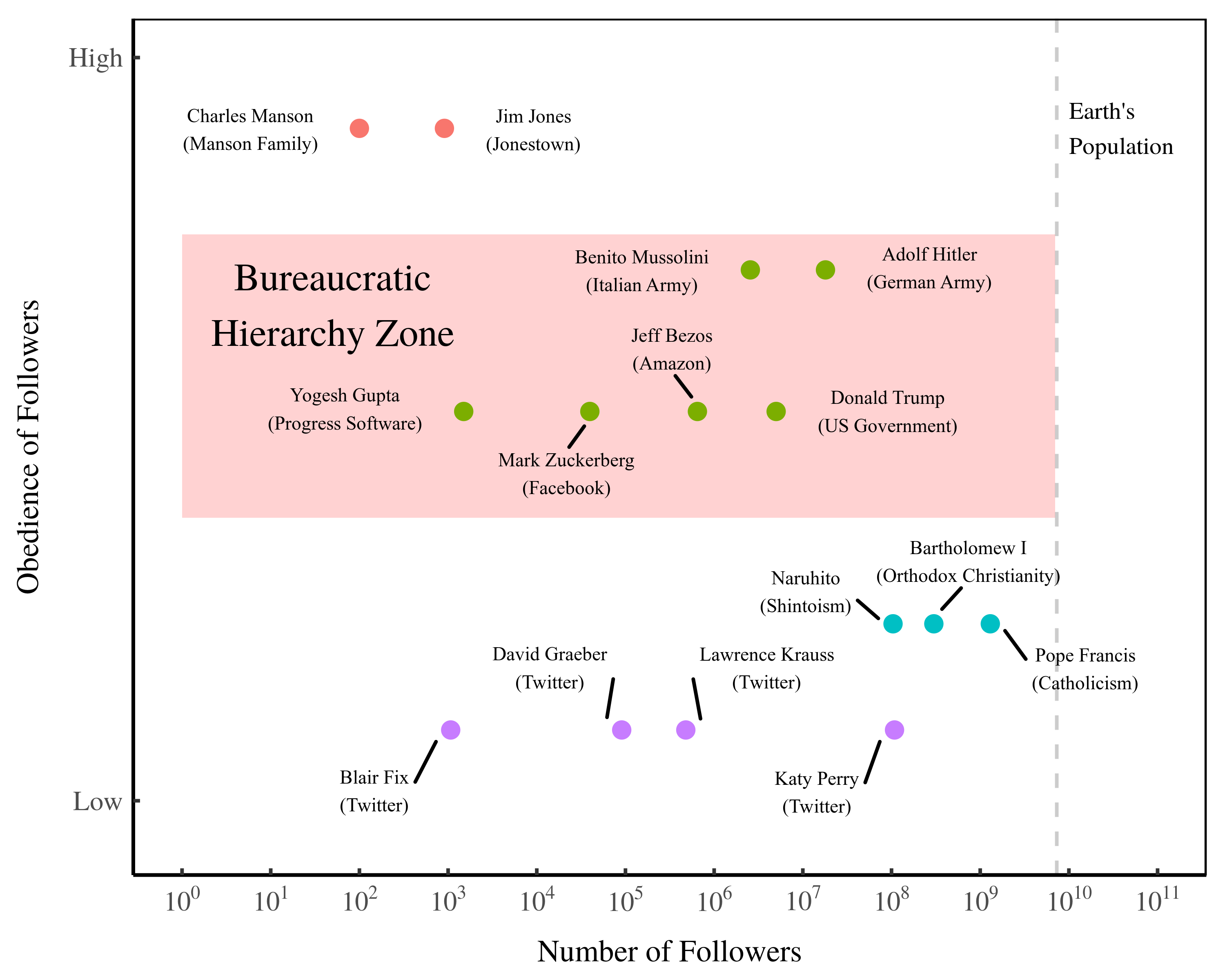
Continue ReadingFix, ‘How the Rich Are Different: Hierarchical Power as the Basis of Income Size and Class’
Abstract This paper investigates a new approach to understanding personal and functional income distribution. I propose that hierarchical power — the command of subordinates in a hierarchy — is what distinguishes the rich from the poor and capitalists from workers. Specifically, I hypothesize that individual income increases with hierarchical power, as does the share of […]
Continue ReadingUnderstanding Income: You Can’t Get There from Here
Originally published on Economics from the Top Down Blair Fix You can’t get the right answer when you ask the wrong question. This truism, I’ve come to believe, explains much of what is wrong with economics. When it comes to studying income, economists ask the wrong question. Economists, I argue, have mostly asked: is income […]
Continue ReadingThe Productivity of Bullshit Jobs
Originally published on Economics from the Top Down Blair Fix I recently read David Graeber’s book Bullshit Jobs: A Theory. If you’re not familiar, David Graeber is the anthropologist who wrote Debt: The First 5000 Years, a seminal book on the history of money and credit. In Bullshit Jobs, Graeber takes aim at pointless work. […]
Continue ReadingAn Evolutionary Theory of Resource Distribution (Part 3)
Originally published on Economics from the Top Down Blair Fix When it comes to earning income in a hierarchy, it’s not what you know that matters. It’s who you control. This was the provocative idea that I proposed in Part 2 of this series on an evolutionary theory of resource distribution. In this post, I […]
Continue ReadingAn Evolutionary Theory of Resource Distribution (Part 2)
Originally published on Economics from the Top Down Blair Fix A 25% chance. That’s the likelihood that when I tell someone I’m searching for a job, they’ll say: Remember, Blair … to land a job, it’s not what you know that matters. It’s who you know. OK, maybe I’m exaggerating this chance. Still, it’s an […]
Continue ReadingAn Evolutionary Theory of Resource Distribution (Part 1)
Originally published on Economics from the Top Down Blair Fix The biologist Theodosius Dobzhansky famously wrote that “nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution”. I propose a corollary in economics: nothing in economics makes sense except in the light of human social evolution. [1] I explore here how the evolution of […]
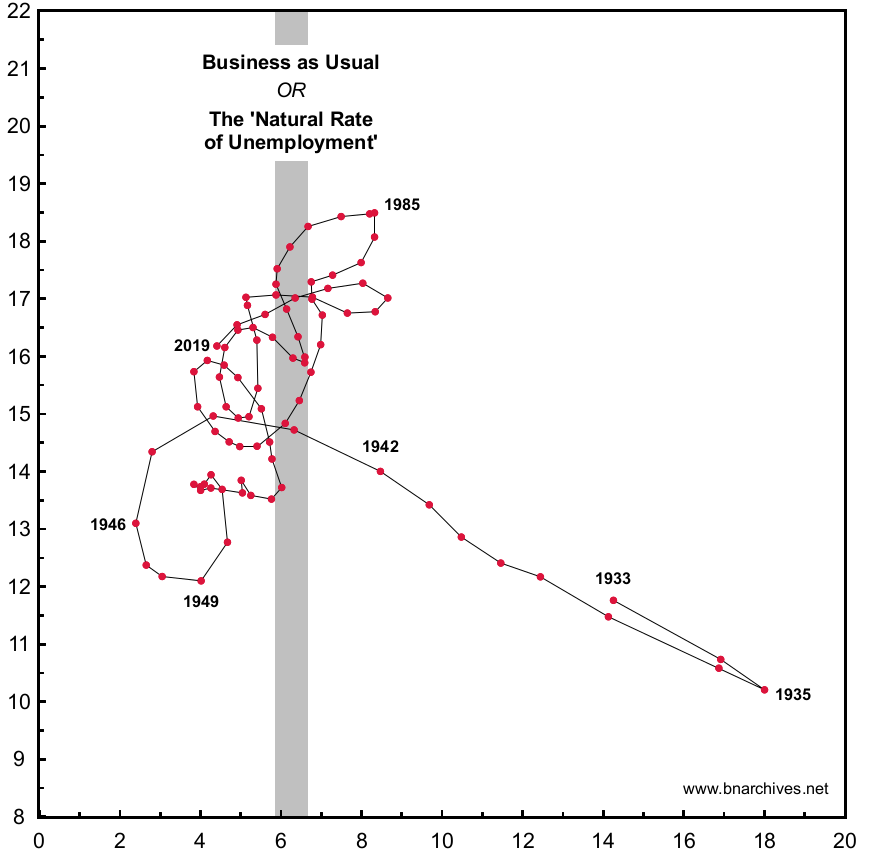
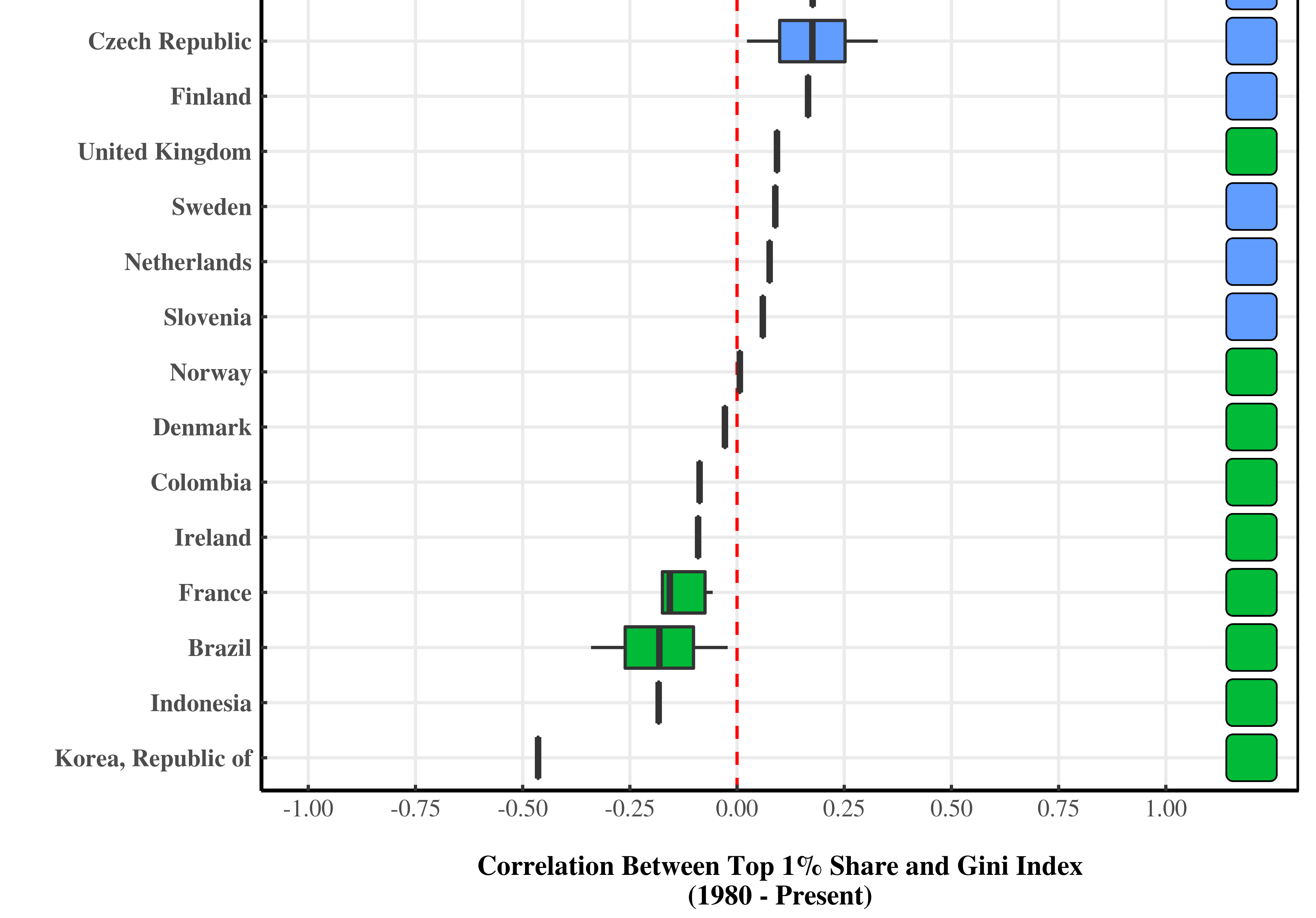
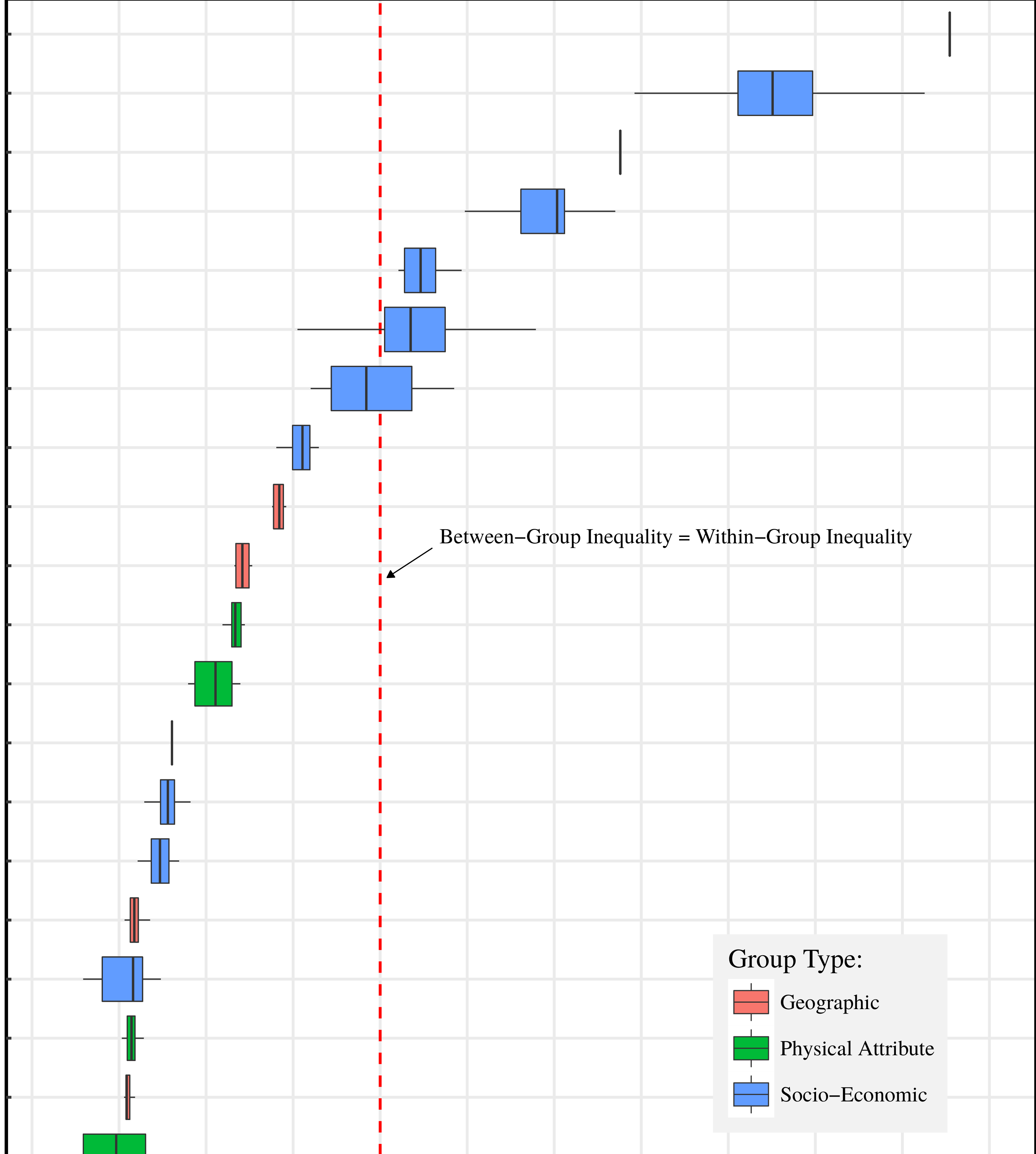
Continue ReadingWhen Inequality Increases and Decreases at the Same Time
Originally published on Economics from the Top Down Blair Fix In Problems With Measuring Inequality, I discussed how inequality is an ambiguous concept. The problem, in short, is that a single metric can never capture every aspect of a distribution of income. Much like we cannot tell the shape of an object from its perimeter […]
Continue ReadingFix, ‘An Evolutionary Theory of Resource Distribution’
Abstract This paper explores how the evolution of human sociality can help us understand how we distribute resources. Using ideas from sociobiology, I argue that resource distribution is marked by a tension between two levels of natural selection. At the group level, selfless behavior is advantageous. But at the individual level, selfish behavior is advantageous. […]
Continue ReadingFix, ‘Personal Income and Hierarchical Power’
Abstract This article examines the relation between personal income and hierarchical power. In the context of a firm hierarchy, I define hierarchical power as the number of subordinates under an individual’s control. Using the available case-study evidence, I find that relative income within firms scales strongly with hierarchical power. I also find that hierarchical power […]
Continue Reading2018/09: Fix, ‘Energy, Hierarchy and the Origin of Inequality’
Abstract Where should we look to understand the origin of inequality? Most research focuses on three windows of evidence: (1) the archaeological record; (2) existing traditional societies; and (3) the historical record. I propose a fourth window of evidence — modern society itself. I hypothesize that we can infer the origin of inequality from the […]
Continue ReadingFix, ‘Economics from the Top Down: Does Hierarchy Unify Economic Theory?’
Abstract What is the unit of analysis in economics? The prevailing orthodoxy in mainstream economic theory is that the individual is the ‘ultimate’ unit of analysis. The implicit goal of mainstream economics is to root macro-level social structure in the micro-level actions of individuals. But there is a simple problem with this approach: our knowledge […]
Continue Reading